 Mind
Mind
- Digital and Modern Well-being
- Mental Health and Emotional Well-being
- Mind-Body Connection and Holistic Health
- Parenting and Family
- Personal Growth and Development
- Relationships and Social Well-being
- Stress and Relaxation
- Therapeutic and Creative Practices
- Trauma and Recovery
- Work, Productivity, and Discipline
 Body
Body
 Fitness
Fitness
 Food
Food
 Beauty
Beauty
Understanding Body Composition
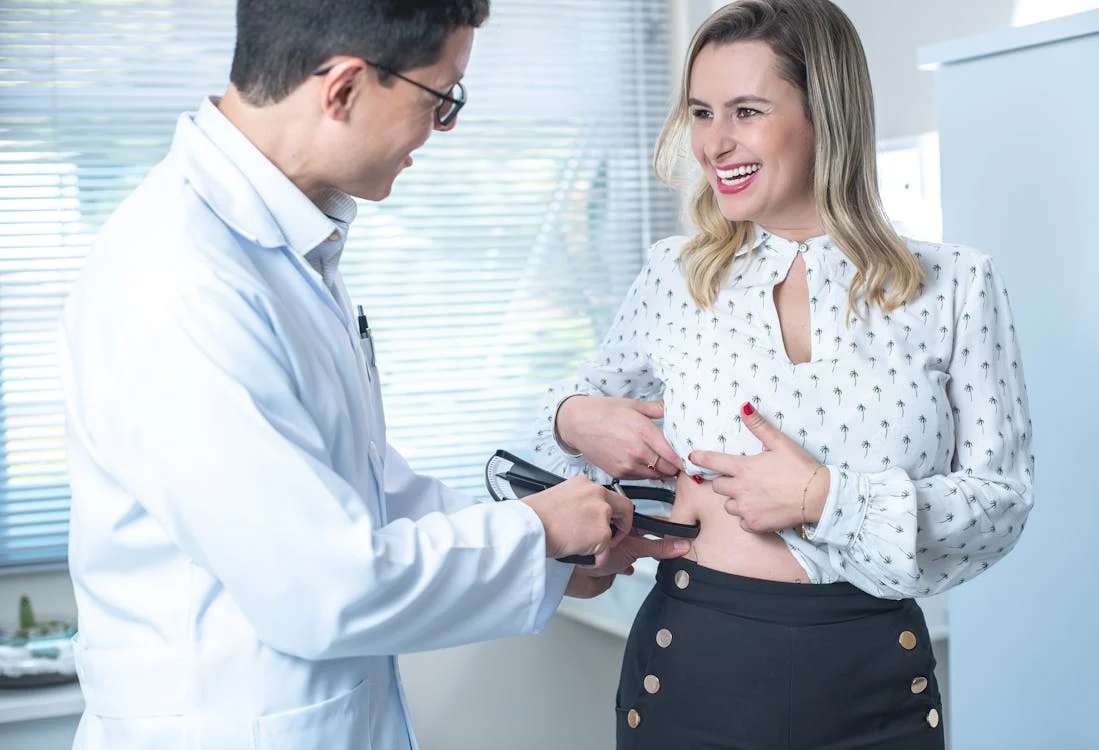

Understanding Body Composition: What It Is and Why It Matters
Body composition is a term that refers to the proportion of fat, muscle, bone, and other tissues that make up the human body. It goes beyond the simple measurement of weight, providing a deeper understanding of an individual’s health and fitness. By examining body composition, we can gain valuable insights into our overall well-being, performance, and risk for various health conditions. This article will explore what body composition is, why it matters, and how it can influence our health and fitness goals.
What Is Body Composition?
Body composition is typically expressed in terms of two main categories: lean body mass and body fat.
Lean Body Mass (LBM): This includes all the components of the body except fat. It encompasses muscles, bones, organs, and fluids. LBM is crucial for various bodily functions, including metabolism, movement, and overall strength.
Body Fat: This is divided into two categories:
- Essential Fat: Necessary for the normal functioning of the body, including insulation and protection for organs. It is essential for hormone production and overall health.
- Storage Fat: The fat stored in adipose tissue, which can be used for energy when needed. While some storage fat is normal, excessive amounts can lead to health issues.
Together, these components provide a clearer picture of an individual’s health than weight alone, helping to assess fitness levels and risks for various diseases.
Why Does Body Composition Matter?
Understanding body composition is vital for several reasons:
1. Health Indicators
Body composition is a better indicator of health than weight alone. For example, two people may weigh the same, but one may have a higher percentage of muscle mass while the other has a higher percentage of body fat. Higher body fat percentages are associated with a greater risk of chronic diseases such as:
- Heart Disease: Excess body fat can lead to higher cholesterol levels, hypertension, and increased risk of heart-related issues.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Higher levels of body fat, particularly visceral fat (fat stored around organs), can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
- Joint Issues: Carrying excess weight can put additional stress on joints, leading to conditions such as osteoarthritis.
2. Fitness and Performance
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, body composition plays a crucial role in performance.
- Muscle Mass: Increased muscle mass can enhance strength, power, and endurance, improving athletic performance.
- Fat Levels: Lower body fat percentages may benefit certain sports, particularly those requiring agility and speed, such as gymnastics or distance running. However, athletes in strength sports may benefit from a higher muscle mass.
Understanding body composition allows individuals to set realistic and tailored fitness goals that align with their performance needs.
3. Weight Management
Body composition assessments can aid in effective weight management strategies. By focusing on fat loss rather than simply weight loss, individuals can achieve healthier body compositions. Strategies include:
- Resistance Training: Building muscle through strength training can increase metabolism and promote fat loss.
- Nutrition: Understanding macronutrient ratios (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) can help tailor diets that support desired body composition goals.
4. Age-Related Changes
As we age, our body composition naturally changes. Muscle mass tends to decrease, while body fat may increase, leading to altered metabolic rates and overall health risks. Monitoring body composition can help older adults maintain healthy muscle levels and mitigate age-related health issues.
5. Psychological Well-Being
Body composition can also impact self-esteem and body image. Understanding one’s body composition can help individuals set realistic goals and foster a healthier relationship with their bodies. It encourages a focus on health and fitness rather than solely on appearance or weight.
How to Assess Body Composition
Several methods are available for assessing body composition, each with its own advantages and limitations. Common methods include:
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): A non-invasive method that estimates body composition by measuring the resistance of body tissues to electrical flow.
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): A highly accurate method that uses low-dose X-rays to differentiate between bone mass, lean mass, and fat mass.
Skinfold Calipers: A method that measures the thickness of skinfolds at specific sites on the body to estimate body fat percentage.
Hydrostatic Weighing: A technique that measures body density by comparing weight on land to weight underwater, providing estimates of body composition.
Circumference Measurements: Simple measurements of waist, hips, and other areas can indicate fat distribution and health risks.
Conclusion
Understanding body composition is crucial for assessing overall health, fitness, and well-being. It provides valuable insights that can guide lifestyle choices, inform fitness and nutrition strategies, and help identify risks for chronic diseases. By focusing on body composition rather than just weight, individuals can work towards healthier, more sustainable goals that enhance their quality of life. Embracing this comprehensive view of health empowers us to make informed choices that promote not just a healthy body but also a healthy mind and spirit.
